NASA, Boeing Test How to Improve Performance of Longer, Narrower Aircraft Wings
5 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
The airliner you board in the future could look a lot different from today’s, with longer, thinner wings that provide a smoother ride while saving fuel.
Those wings would be a revolutionary design for commercial aircraft, but like any breakthrough technology, they come with their own development challenges – which experts from NASA and Boeing are now working to solve.
When creating lift, longer, thinner wings can reduce drag, making them efficient. However, they can become very flexible in flight.
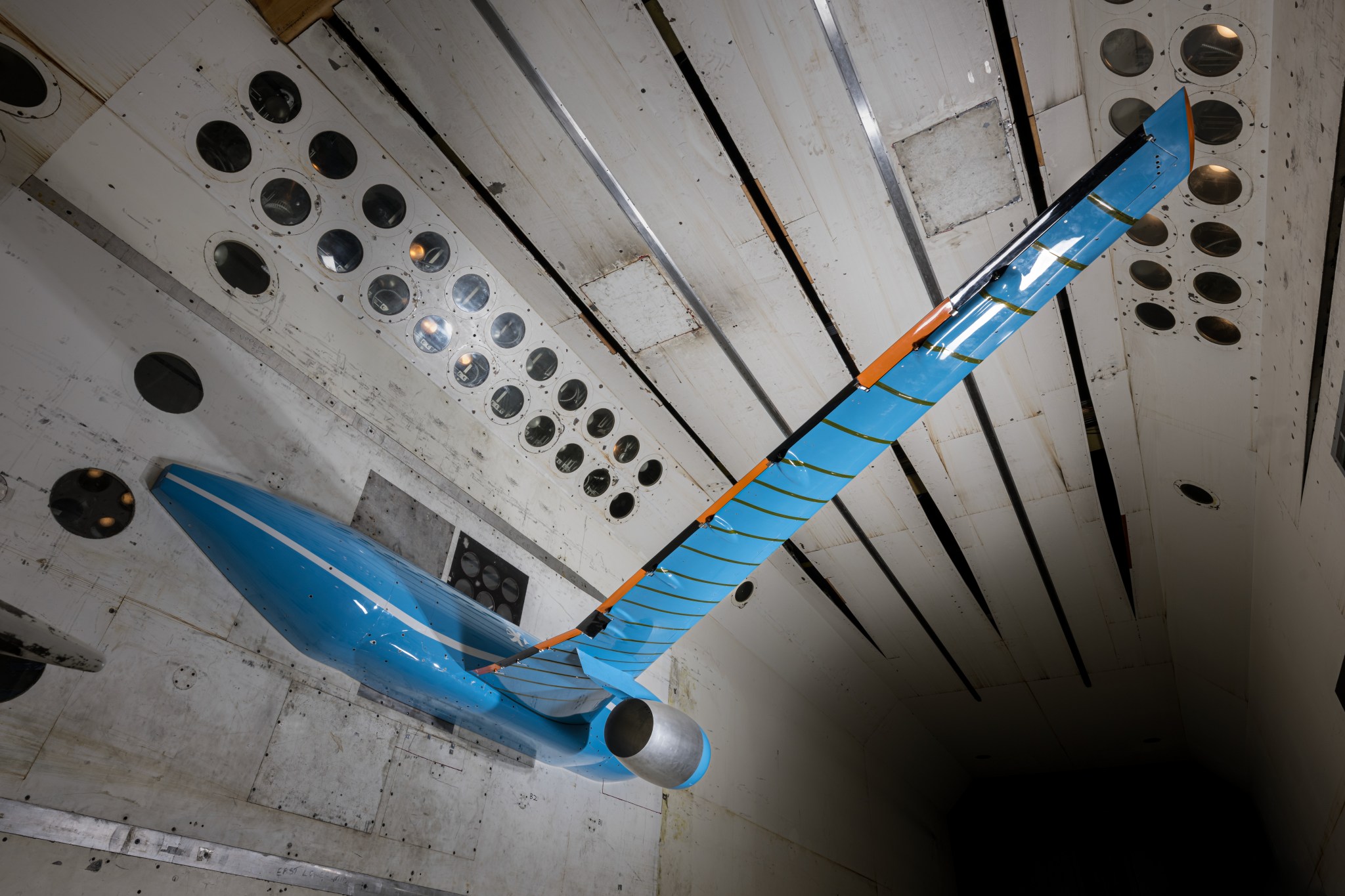
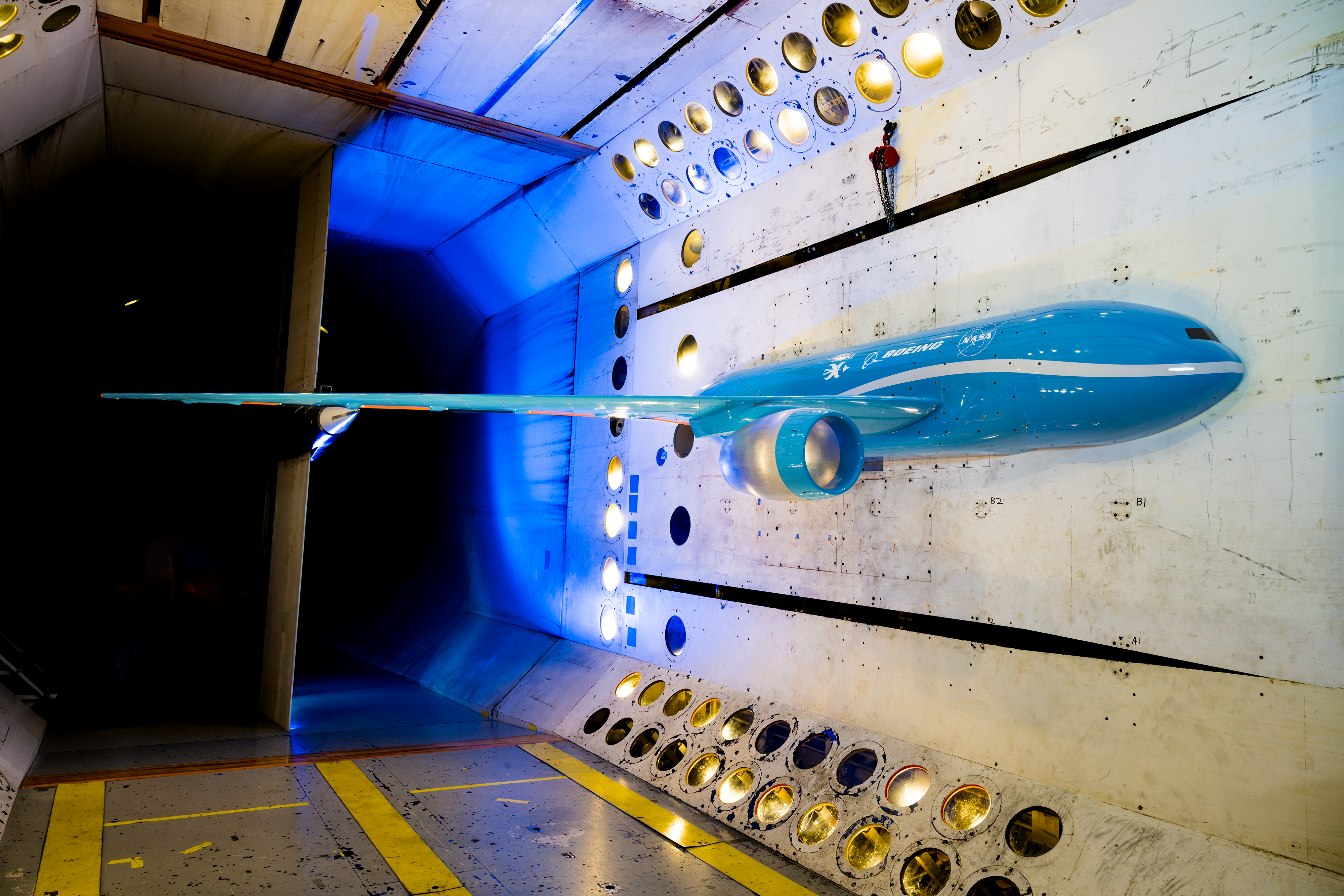
Through their Integrated Adaptive Wing Technology Maturation collaboration, NASA and Boeing recently completed wind tunnel tests of a “higher aspect ratio wing model” looking for ways to get the efficiency gains without the potential issues these kinds of wings can experience.
“When you have a very flexible wing, you’re getting into greater motions,” said Jennifer Pinkerton, a NASA aerospace engineer at NASA Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. “Things like gust loads and maneuver loads can cause even more of an excitation than with a smaller aspect ratio wing. Higher aspect ratio wings also tend to be more fuel efficient, so we’re trying to take advantage of that while simultaneously controlling the aeroelastic response.”
Without the right engineering, long, thin wings could potentially bend or experience a condition known as wing flutter, causing aircraft to vibrate and shake in gusting winds.
“Flutter is a very violent interaction,” Pinkerton said. “When the flow over a wing interacts with the aircraft structure and the natural frequencies of the wing are excited, wing oscillations are amplified and can grow exponentially, leading to potentially catastrophic failure. Part of the testing we do is to characterize aeroelastic instabilities like flutter for aircraft concepts so that in actual flight, those instabilities can be safely avoided.”
To help demonstrate and understand this, researchers from NASA and Boeing sought to soften the impacts of wind gusts on the aircraft, lessen the wing loads from aircraft turns and movements, and suppress wing flutter.
Reducing or controlling those factors can have a significant impact on an aircraft’s performance, fuel efficiency, and passenger comfort.
Testing for this in a controlled environment is impossible with a full-sized commercial airliner, as no wind tunnel could accommodate one.
However, NASA Langley’s Transonic Dynamics Tunnel, which has been contributing to the design of U.S. commercial transports, military aircraft, launch vehicles, and spacecraft for over 60 years, features a test section 16 feet high by 16 feet wide, big enough for large-scale models.
To shrink a full-size plane down to scale, NASA and Boeing worked with NextGen Aeronautics, which designed and fabricated a complex model resembling an aircraft divided down the middle, with one 13-foot wing.
Mounted to the wall of the wind tunnel, the model was outfitted with 10 control surfaces – moveable panels – along the wing’s rear edge. Researchers adjusted those control surfaces to control airflow and reduce the forces that were causing the wing to vibrate.
Instruments and sensors mounted inside the model measured the forces acting on the model, as well as the vehicle’s responses.
The model wing represented a leap in sophistication from a smaller one developed during a previous NASA-Boeing collaboration called the Subsonic Ultra Green Aircraft Research (SUGAR).
“The SUGAR model had two active control surfaces,” said Patrick S. Heaney, principal investigator at NASA for the Integrated Adaptive Wing Technology Maturation collaboration. “And now on this particular model we have ten. We’re increasing the complexity as well as expanding what our control objectives are.”
A first set of tests, conducted in 2024, gave experts baseline readings that they compared to NASA computational simulations, allowing them to refine their models. A second set of tests in 2025 used the additional control surfaces in new configurations.
The most visible benefits of these new capabilities appeared during testing to alleviate the forces from gusting winds, when researchers saw the wing’s shaking greatly reduced.
With testing completed, NASA and Boeing experts are analyzing data and preparing to share their results with the aviation community. Airlines and original equipment manufacturers can learn and benefit from the lessons learned, deciding which to apply to the next generation of aircraft.
“Initial data analyses have shown that controllers developed by NASA and Boeing and used during the test demonstrated large performance improvements,” Heaney said. “We’re excited to continue analyzing the data and sharing results in the months to come.”
NASA’s Advanced Air Transport Technology project works to advance aircraft design and technology under the agency’s Advanced Air Vehicles program, which studies, evaluates, and develops technologies and capabilities for new aircraft systems. The project and program fall within NASA’s Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate.
Explore More
Discover More Topics From NASA