NASA Armstrong Advances Flight Research and Innovation in 2025
12 min read
Preparations for Next Moonwalk Simulations Underway (and Underwater)
In 2025, NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, advanced work across aeronautics, Earth science, exploration technologies, and emerging aviation systems, reinforcing its role as one of the agency’s primary test sites for aeronautics research. From early concept evaluations to full flight test campaigns, teams enhanced measurement tools, refined safety systems, and generated data that supported missions across NASA. Operating from the Mojave Desert, NASA Armstrong continued applying engineering design with real-world performance, carrying forward research that informs how aircraft operate today and how new systems may function in the future.
The year’s progress also reflects the people behind the work – engineers, technicians, pilots, operators, and mission support staff who navigate complex tests and ensure each mission advances safely and deliberately. Their efforts strengthened partnerships with industry, small businesses, and universities while expanding opportunities for students and early career professionals. Together they sustained NASA Armstrong’s long-standing identity as a center where innovation is proven in flight and where research helps chart the course for future aviation and exploration.
“We executed our mission work safely, including flight of the first piloted NASA X-plane in decades, while under challenging conditions,” said Brad Flick, center director of NASA Armstrong. “It tells me our people embrace the work we do and are willing to maintain high levels of professionalism while enduring personal stress and uncertainty. It’s a testimony to the dedication of our NASA and contractor workforce.”
Teams continued advancing key projects, supporting partners, and generating data that contributes to NASA’s broader mission.
Quiet supersonic flight and the Quesst mission

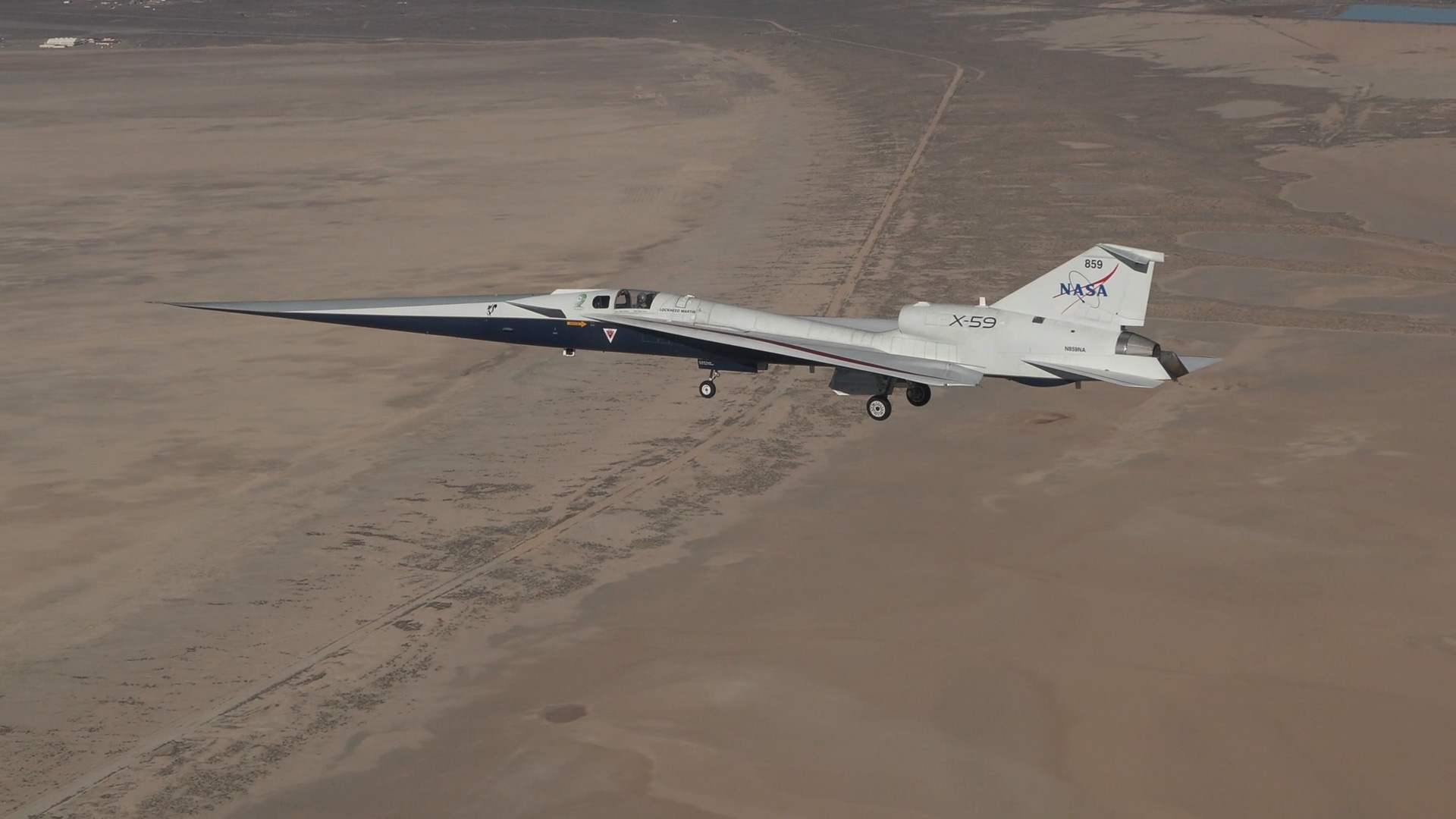
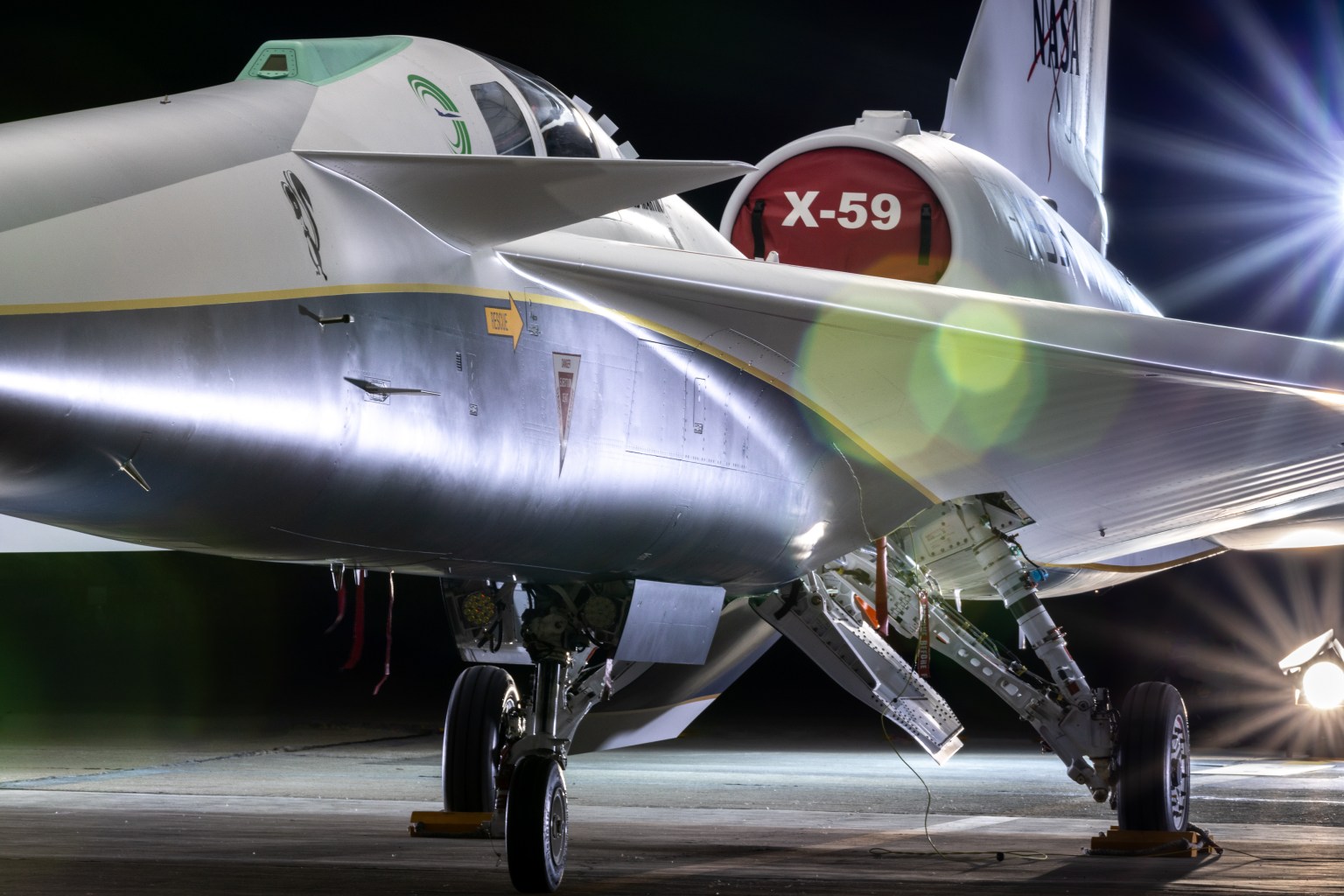
NASA Armstrong continued its quiet supersonic research, completing a series of activities in support of NASA’s Quesst mission. On the X-59 quiet supersonic research aircraft, the team performed electromagnetic interference tests and ran engine checks to prepare the aircraft for taxi tests. The Schlieren, Airborne Measurements, and Range Operations for Quesst (SCHAMROQ) team completed aircraft integration and shock-sensing probe calibration flights, refining the tools needed to characterize shock waves from the X-59. These efforts supported the aircraft’s progression toward its first flight on Oct. 28, marking a historic milestone and the beginning of its transition to NASA Armstrong for continued testing.
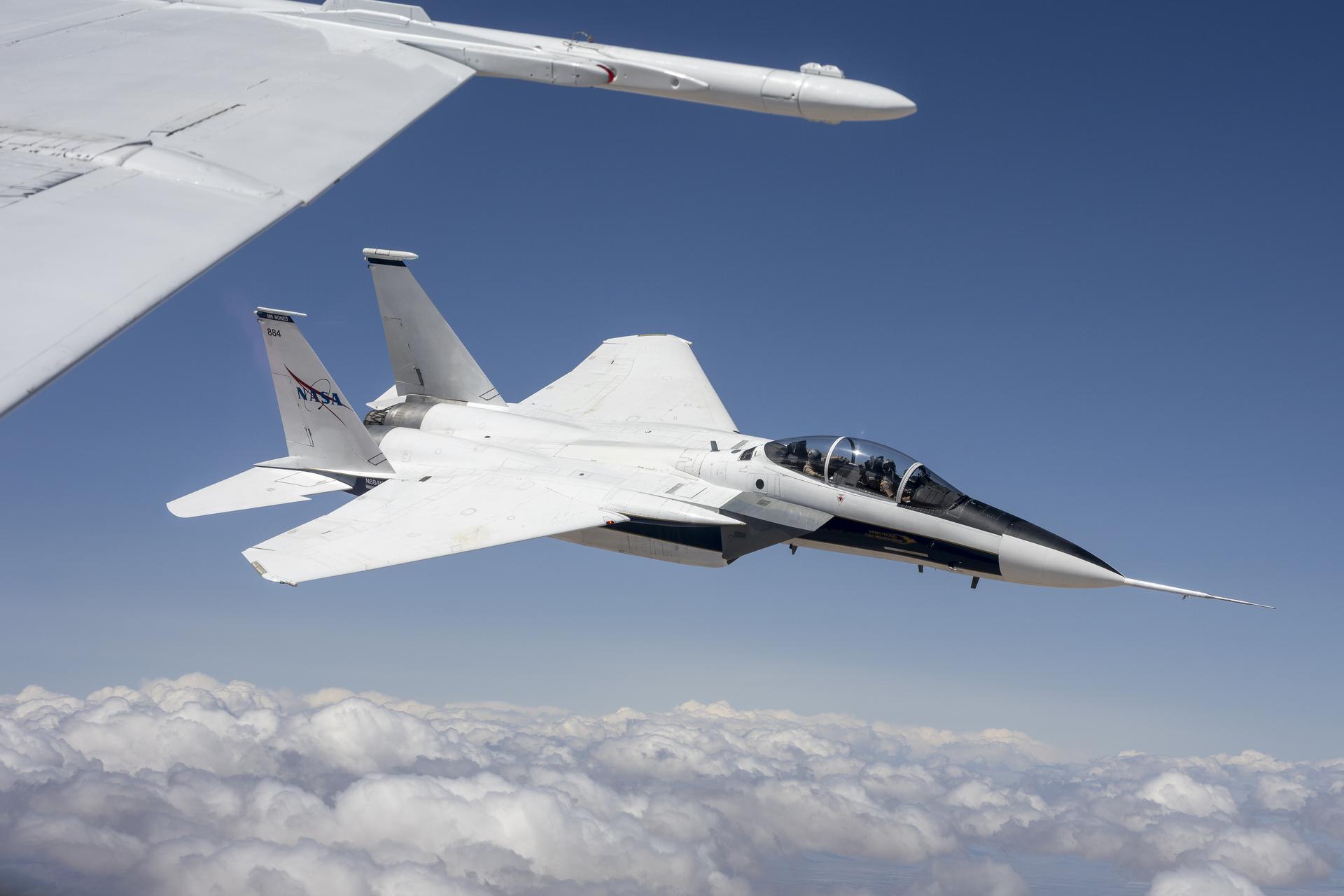
The center’s Commercial Supersonic Technology (CST) team also conducted airborne validation flights using NASA F-15s, confirming measurement systems essential for Quesst’s next research phase. Together, this work forms the technical backbone for upcoming community response studies, where NASA will evaluate whether quieter supersonic thumps could support future commercial applications.
- The X-59 team completed electromagnetic interference testing on the aircraft, verifying system performance and confirming that all its systems could reliably operate together.
- NASA’s X-59 engine testing concluded with a maximum afterburner test that demonstrated the engine’s ability to generate the thrust required for supersonic flight.
- Engineers conducted engine speed-hold evaluations to assess how the X-59’s engine responds under sustained throttle conditions, generating data used to refine control settings for upcoming flight profiles.
- NASA Armstrong’s SCHAMROQ team calibrated a second shock-sensing probe to expand measurement capability for future quiet supersonic flight research.
- NASA Armstrong’s CST team validated the tools that will gather airborne data in support the second phase of the agency’s Quesst mission.
- NASA’s X-59 team advanced preparations on the aircraft through taxi tests, ensuring aircraft handling systems performed correctly ahead of its first flight.
- NASA Armstrong’s photo and video team documented X-59 taxi tests as the aircraft moved under its own power for the first time.
- The X-59 team evaluated braking, steering, and integrated systems performance after the completion of the aircraft’s low-speed taxi tests marking one of the final steps before flight.
- NASA Armstrong teams advanced the X-59 toward first flight by prioritizing safety at every step, completing checks, evaluations, and system verifications to ensure the aircraft was ready when the team was confident it could move forward.
- NASA and the Lockheed Martin contractor team completed the X-59’s historic first flight, delivering the aircraft to NASA Armstrong for the start of its next phase of research.
Ultra-efficient and high-speed aircraft research

Across aeronautics programs, Armstrong supported work that strengthens NASA’s ability to study sustainable, efficient, and high-performance aircraft. Teams conducted aerodynamic measurements and improved test-article access for instrumentation, enabling more precise evaluations of advanced aircraft concepts. Engineers continued developing tools and techniques to study aircraft performance under high-speed and high-temperature conditions, supporting research in hypersonic flight.
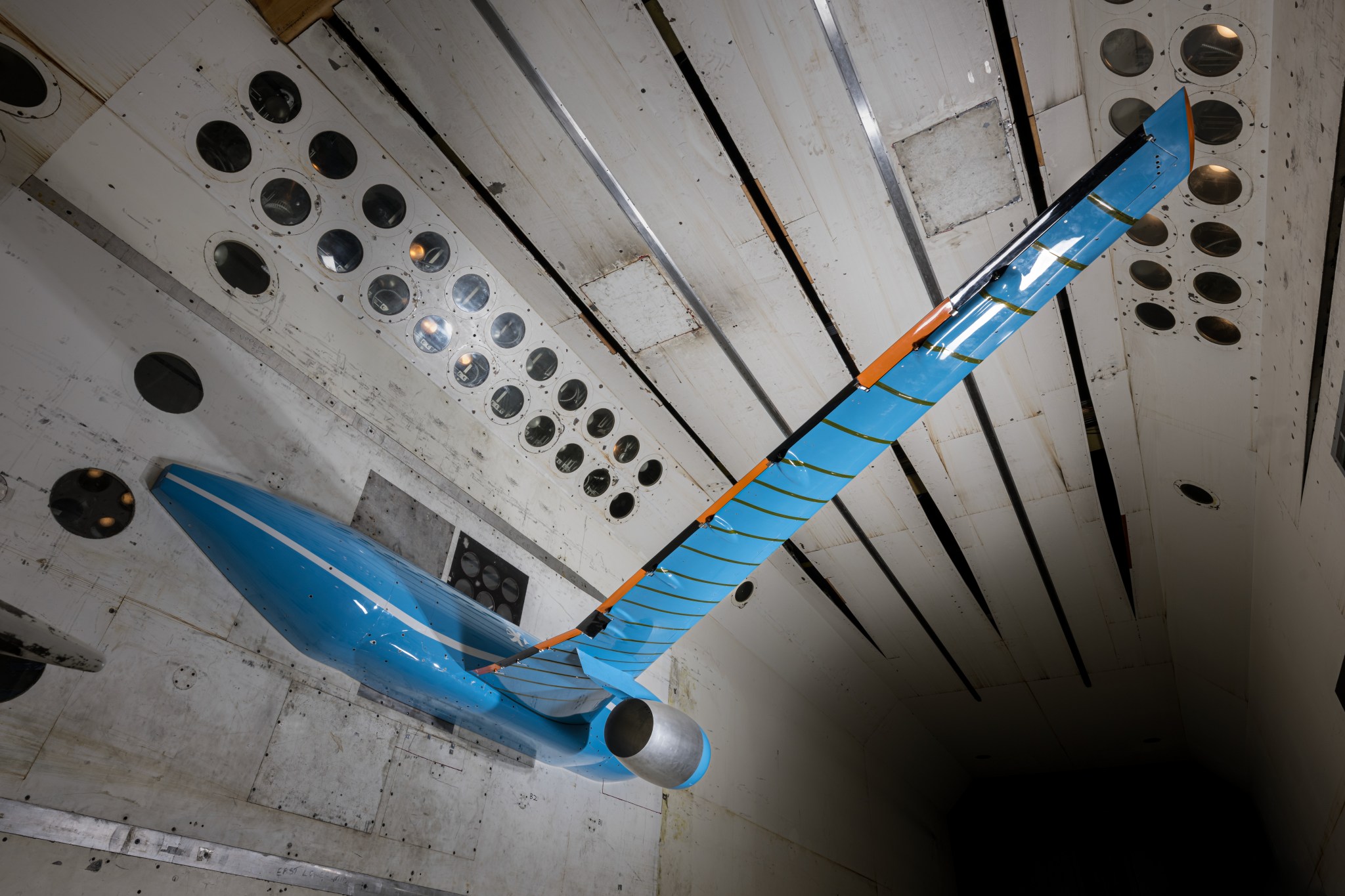
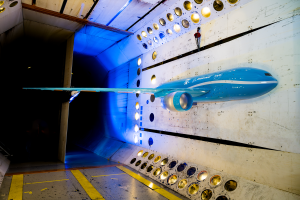
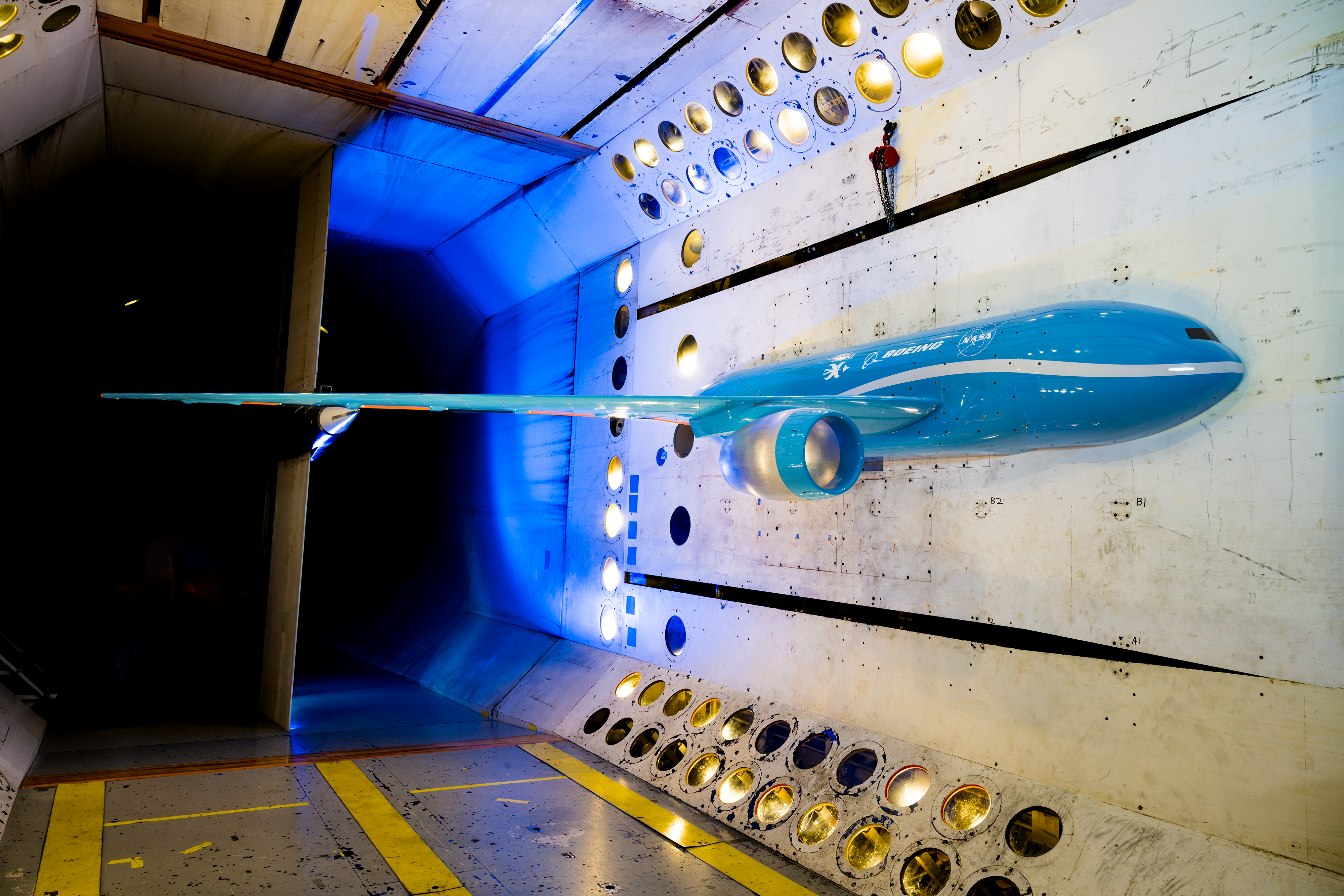
- The Sustainable Flight Demonstrator research team measured airflow over key wing surfaces in a series of wind tunnel tests, generating data used to refine future sustainable aircraft designs.
- Technicians at NASA Armstrong installed a custom structural floor inside the X-66 demonstrator, improving access for instrumentation work and enabling more efficient modification and evaluation.
- Armstrong engineers advanced high-speed research by maturing an optical measurement system that tracks heat and structural strain during hypersonic flight, supporting future test missions.
Transforming air mobility and new aviation systems
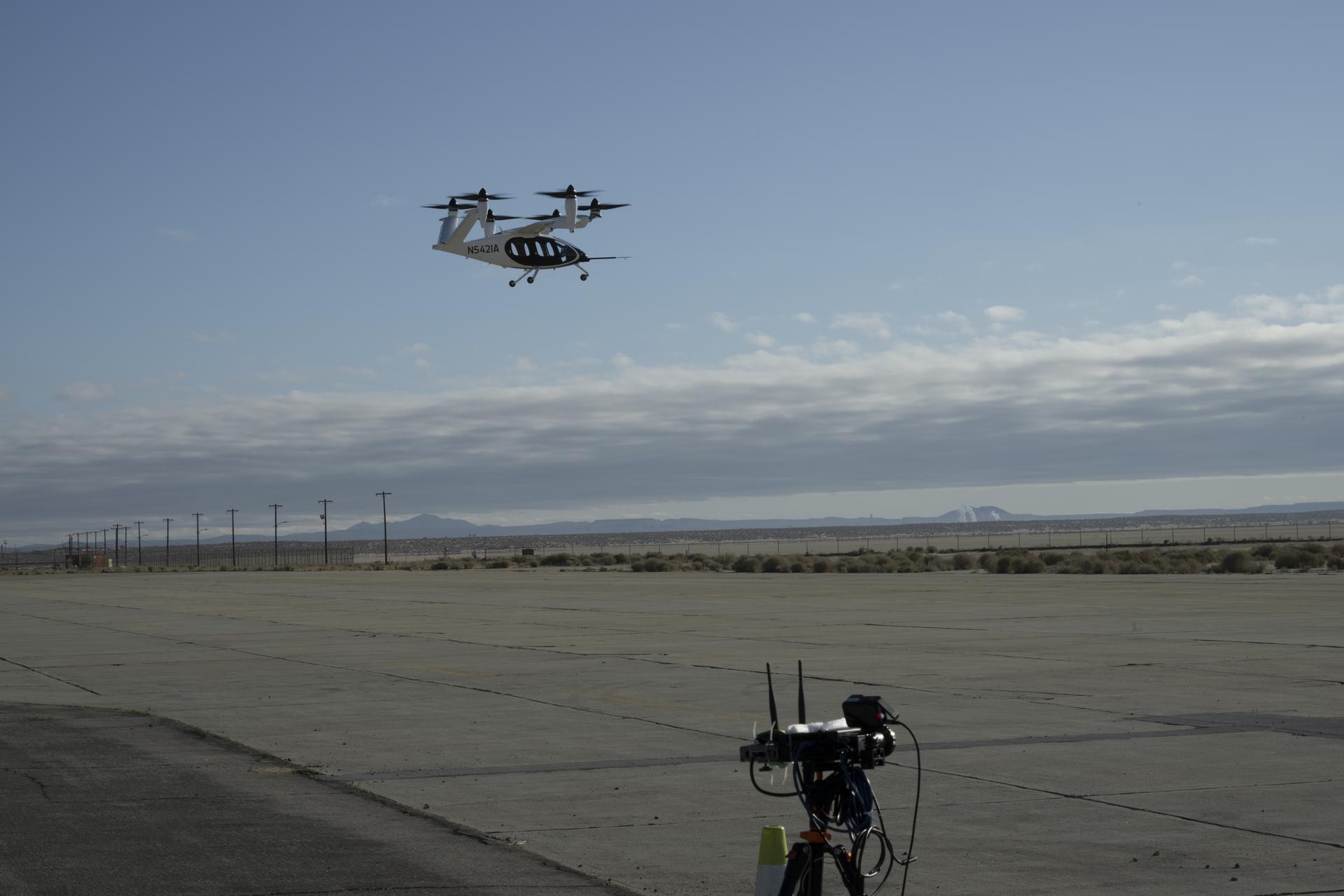

NASA Armstrong supported multiple aspects of the nation’s growing air mobility ecosystem. Researchers conducted tests and evaluations to better understand aircraft performance, airflow, and passenger experience. Additional work included assessing drone-based inspection techniques, developing advanced communication networks, performing drop tests, and refining methods to evaluate emerging mobility aircraft.
These studies support NASA’s broader goal of integrating new electric, autonomous, and hybrid aircraft safely into the national airspace.
- A small business partnership demonstrated drone-based inspection techniques that could reduce maintenance time and improve safety for commercial aircraft operations.
- NASA Armstrong researchers tested air traffic surveillance technology against the demands of air taxis flying at low altitudes through densely populated cities, using the agency’s Pilatus PC-12 to support safer air traffic operations.
- Researchers at NASA Armstrong collected airflow data from Joby using a ground array of sensors to examine how its circular wind patterns might affect electric air taxi performance in future urban operations.
- NASA Armstrong’s Ride Quality Laboratory conducted air taxi passenger comfort studies in support of the agency’s Advanced Air Mobility mission to better understand how motion, vibration, and other factors affect ride comfort, informing the industry’s development of electric air taxis and drones.
Earth observation and environmental research

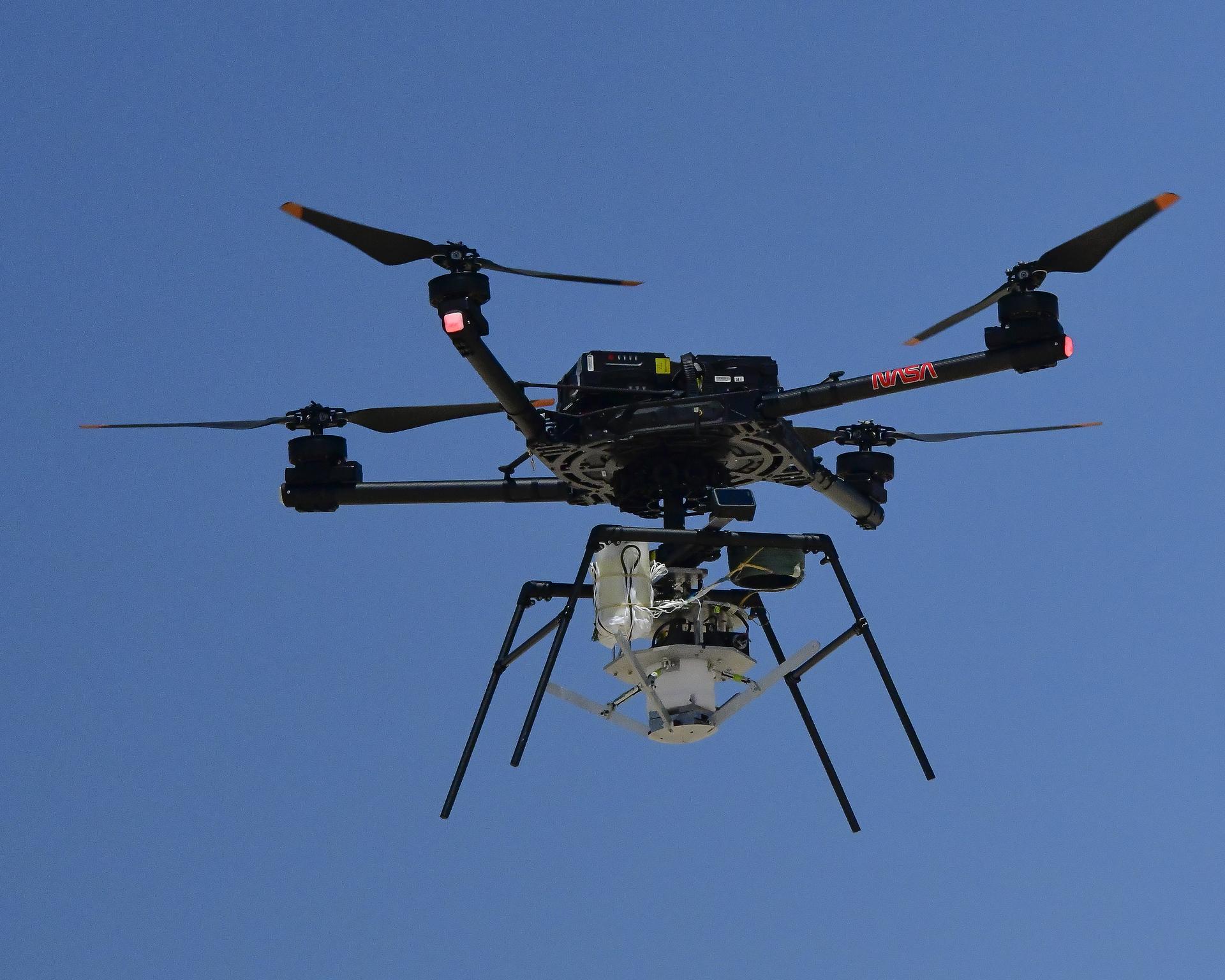
Earth science campaigns at NASA Armstrong contributed to the agency’s ability to monitor environmental changes and improve satellite data accuracy. Researchers tested precision navigation systems that keep high-speed aircraft on path, supporting more accurate atmospheric and climate surveys. Airborne measurements and drone flights documented wildfire behavior, smoke transport, and post-fire impacts while gathering temperature, humidity, and airflow data during controlled burns. These efforts also supported early-stage technology demonstrations, evaluating new wildfire sensing tools under real flight conditions to advance fire response research. High-altitude aircraft contributed to missions that improved satellite calibration, refined atmospheric measurements, and supported snowpack and melt studies to enhance regional water-resource forecasting.
- Researchers at NASA Armstrong tested a new precision‑navigation system that can keep high‑speed research aircraft on exact flight paths, enabling more accurate Earth science data collection during airborne environmental and climate‑survey missions.
- NASA’s B200 King Air flew over wildfire‑affected regions equipped with the Compact Fire Infrared Radiance Spectral Tracker (c‑FIRST), collecting thermal‑infrared data to study wildfire behavior, smoke spread, and post‑fire ecological impacts in near real time.
- NASA Armstrong’s Alta X drone carried a 3D wind sensor and a radiosonde to measure temperature, pressure, humidity, and airflow during a prescribed burn in Geneva State Forest, gathering data to help improve wildland fire behavior models and support firefighting agencies.
- NASA’s ER‑2 aircraft carried the Airborne Lunar Spectral Irradiance (air-LUSI) instrument on night flights, measuring moonlight reflectance to generate calibration data – improving the accuracy of Earth‑observing satellite measurements.
- The center’s ER-2 also flew above cloud layers with specialized instrumentation to collect atmospheric and cloud measurements. These data help validate and refine Earth observing satellite retrievals, improving climate, weather, and aerosol observations.
- Airborne campaigns at NASA Armstrong measured snowpack and melt patterns in the western U.S., providing data to improve water-resource forecasting for local communities.
Exploration technology and Artemis support

NASA Armstrong supported exploration technologies that will contribute to agency’s return to the Moon and future missions deeper into the solar system, including sending the first astronauts – American astronauts – to Mars. Teams advanced sensor systems and conducted high-altitude drop tests to capture critical performance data, supporting the need for precise entry, descent, and landing capabilities on future planetary missions.
Contributions from NASA Armstrong also strengthen the systems and technologies that help make Artemis – the agency’s top priority – safer, more reliable, and more scientifically productive, supporting a sustained human presence on the Moon and preparing for future human exploration of Mars.
- The EPIC team at NASA Armstrong conducted research flights to advance sensor technology for supersonic parachute deployments, evaluating performance during high-speed, high-altitude drops relevant to future planetary missions.
- Imagery from the EPIC test flights at NASA Armstrong highlights the parachute system’s high-altitude deployment sequence and demonstrated its potential for future Mars delivery concepts.
People, workforce, and community engagement
The center expanded outreach, education, and workforce development efforts throughout the year. Students visited NASA Armstrong for hands-on exposure to careers in aeronautics, while staff and volunteers supported a regional robotics competition that encouraged exploration of the field. Educators brought aeronautics concepts directly into classrooms across the region, and interns from around the country gained experience supporting real flight research projects.
NASA Armstrong also highlighted unique career pathways and recognized employees whose work showcases the human side of NASA missions. A youth aviation program launched with a regional museum provided additional opportunities for young learners to explore flight science, further strengthening the center’s community impact:
- Students from Palmdale High School Engineering Club visited NASA Armstrong, where staff engaged with them to explore facilities, discuss aerospace work, and promote STEM careers as part of the center’s community outreach.
- NASA Armstrong staff and volunteers mentored high school teams at the 2025 Aerospace Valley FIRST Robotics Competition, helping students build and test robots and providing hands-on experience with engineering to foster interest in STEM careers.
- In April, NASA Armstrong expanded outreach in 2025 by bringing aeronautics concepts to students through classroom workshops, presentations, and hands-on activities, giving young learners direct exposure to NASA research and inspiring possible future careers in science and engineering.
- Students from across the country participated in internships at NASA Armstrong, gaining hands-on experience in flight research and operations while contributing to real-world aerospace projects.
- In May, a NASA Armstrong videographer earned national recognition for work that highlights the people behind the center’s research missions, showing how scientists, engineers, and flight crews collaborate to advance aeronautics and space exploration.
- Daniel Eng, a systems engineer with NASA’s Air Mobility Pathfinders project, shared his career path from the garment industry to aerospace, illustrating how diverse experiences contribute to the center’s technical workforce and support its advanced flight research and engineering projects.
- In June, NASA Armstrong recognized one of its interns for hands-on work with the center’s aircraft. With more than a decade in the auto industry, they demonstrated how early career engineers can gain real-world experience and develop skills for careers in aerospace and flight research.
- NASA Armstrong partnered with a regional museum to create a youth aviation program that introduces students to flight science and operations, providing hands-on learning opportunities and inspiring interest in aerospace and STEM careers.
Center infrastructure and research capabilities
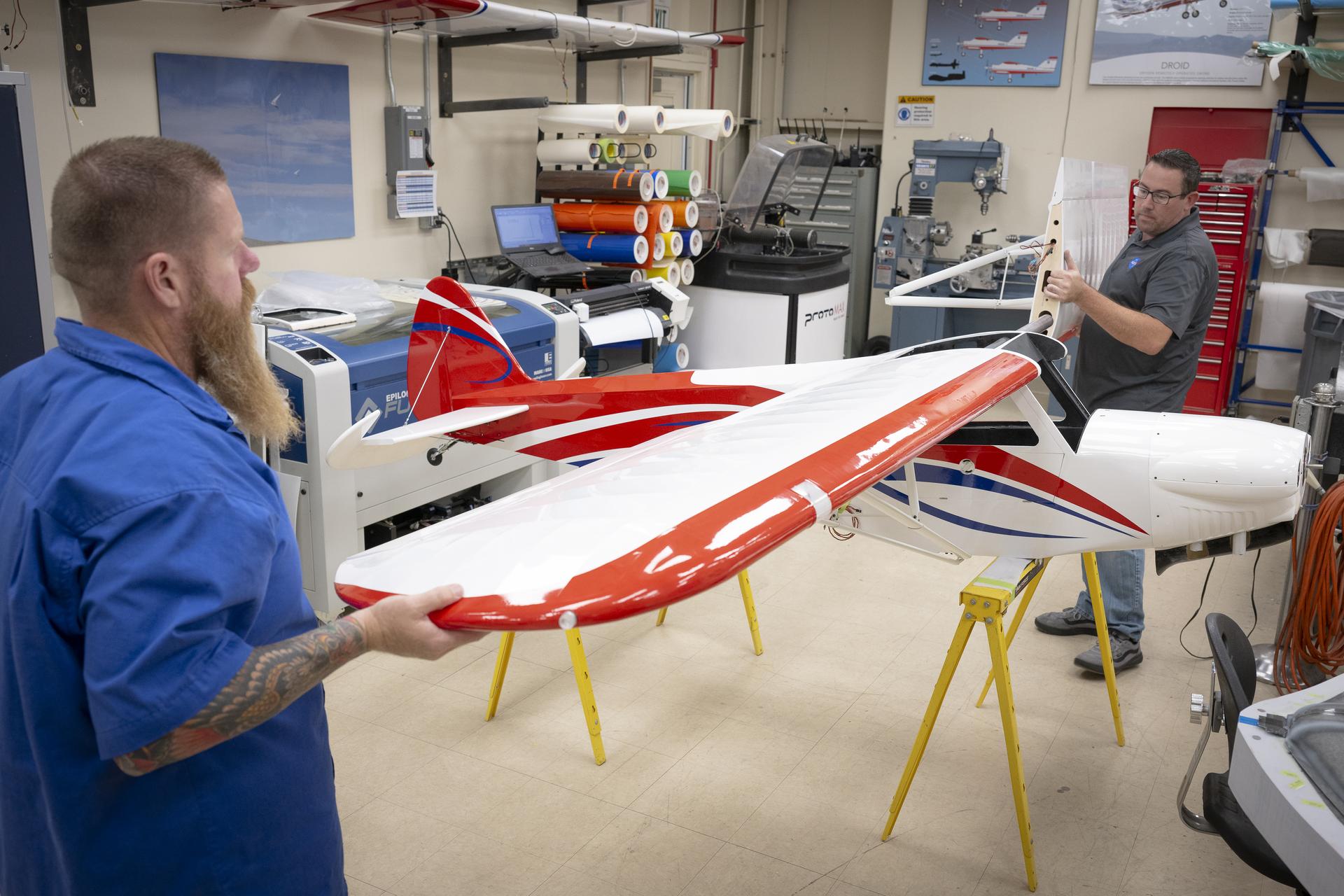

Facility improvements and new platforms strengthened NASA Armstrong’s research capabilities. A rooftop operation removed a historic telemetry pedestal to make way for updated infrastructure, while preserving an important artifact of the center’s flight test heritage. Engineers also completed a new subscale research aircraft, providing a flexible, cost-effective platform for evaluating aerodynamics, instrumentation, and flight control concepts in preparation for full-scale testing:
- The center improved workspace access and supported a re-roofing project during a helicopter crew operation that removed a 2,500-pound telemetry pedestal from a building rooftop, preserving a piece of the center’s flight history heritage.
- Engineers at NASA Armstrong built a new subscale experimental aircraft to replace the center’s aging MicroCub. The 14-foot wingspan, 60-pound aircraft provides a flexible, cost-effective platform for testing aerodynamics, instrumentation, and flight control concepts while reducing risk before full-scale or crewed flight tests.
Looking ahead
NASA Armstrong will continue advancing flight research across aeronautics and Earth science, building on this year’s achievements. Upcoming efforts include additional X-59 flights, expanded quiet supersonic studies, new air mobility evaluations, high-altitude science campaigns, and maturing technologies that support hypersonic research and the Artemis program for future planetary missions.
“Next year will be a year of continuity, but also change,” Flick said. “The agency’s new Administrator, Jared Isaacman, will bring a renewed mission-first focus to the agency, and NASA Armstrong will push the boundaries of what’s possible. But the most important thing we can do is safely and successfully execute our portfolio of work within budget and schedule.”
For more than seven decades, NASA Armstrong has strengthened the nation’s understanding of flight. This year’s work builds on that legacy, helping shape the future of aviation and exploration through research proven in the air.
To explore more about NASA Armstrong’s missions, research, and discoveries, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/armstrong
Details
Explore More
Discover More Topics From NASA