Out of This World Discoveries: Space Station Research in 2025
Out of This World Discoveries: Space Station Research in 2025

As Earth completed its orbit around the Sun to close out 2025, the International Space Station circled our planet more than 5,800 times. Serving as humanity’s unique laboratory in space, the station has hosted thousands of experiments and technology demonstrations, advancing science in ways that cannot be replicated on Earth.
In 2025 alone, more than 750 experiments supported exploration missions, improved life on Earth, and opened commercial opportunities in low Earth orbit. The space station continues to drive innovation by enabling human exploration of the Moon and Mars, transforming medical research, deepening our understanding of the universe, and fostering a growing commercial economy.
Read through just a handful of 2025’s innovative research achievements from the orbiting laboratory.
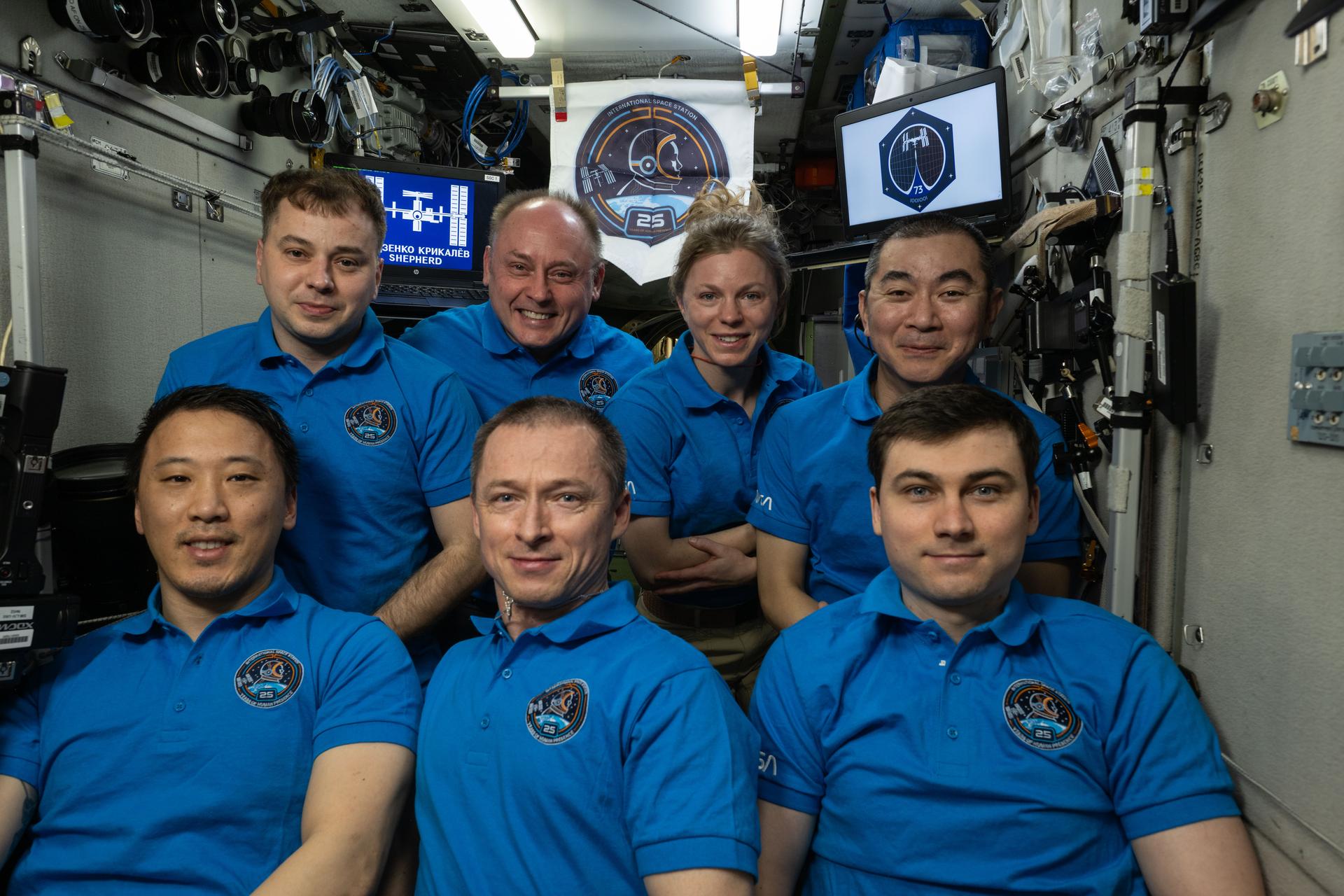
25 Years of humans researching in orbit
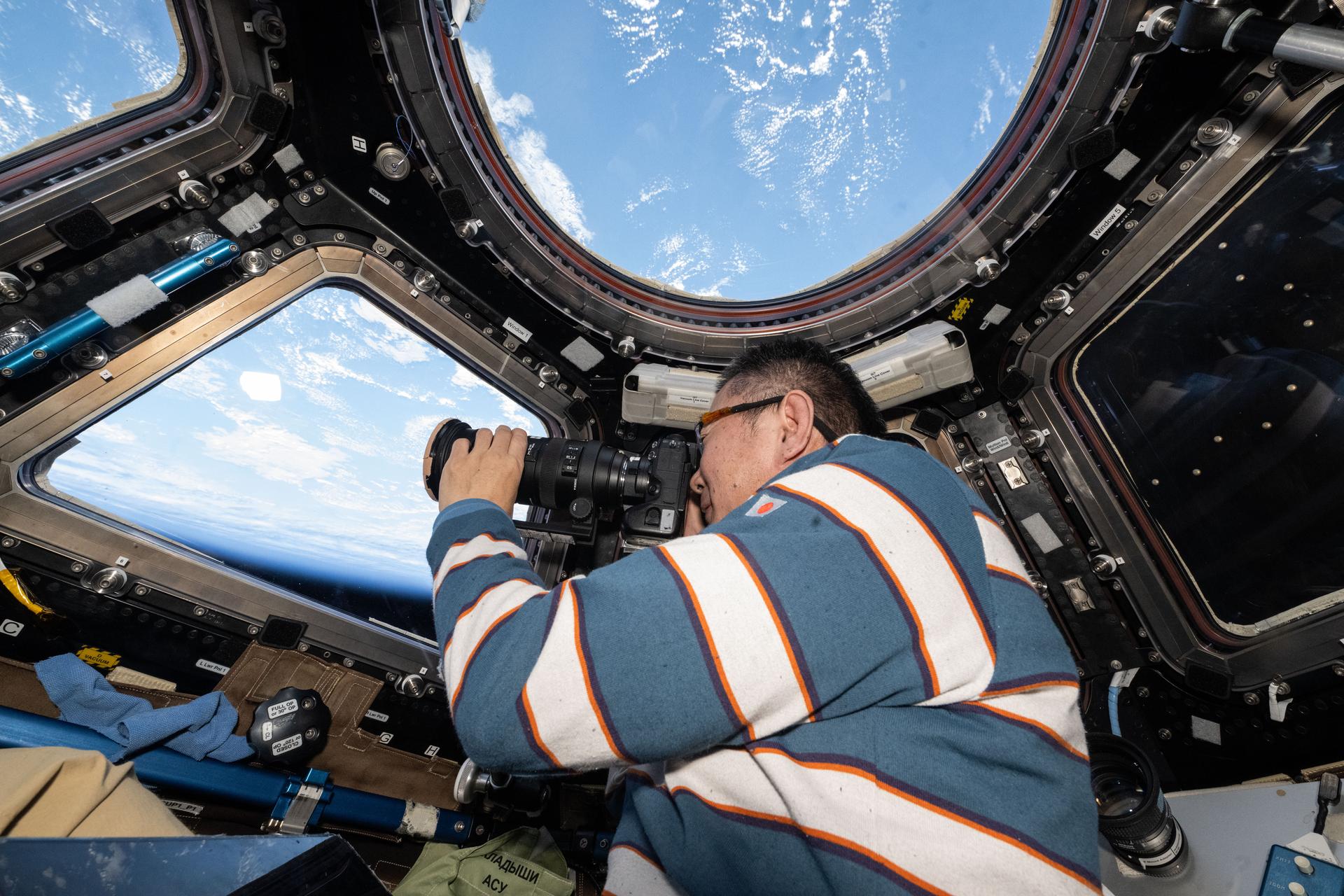
On Nov. 2, 2025, humanity reached a milestone of cosmic proportions: 25 years of continuous human presence aboard the International Space Station. Since the first crew arrived on Nov. 2, 2000, NASA and its partners from around the world have conducted more than 4,000 research investigations and technology demonstrations. More than 290 people from 26 countries have visited the space station, where continuous human presence enables research that surpasses the capabilities of satellites and autonomous platforms. The space station’s unique microgravity environment, paired with crew operations, continues to unlock discoveries and push the boundaries of humanity’s curiosity and innovation.
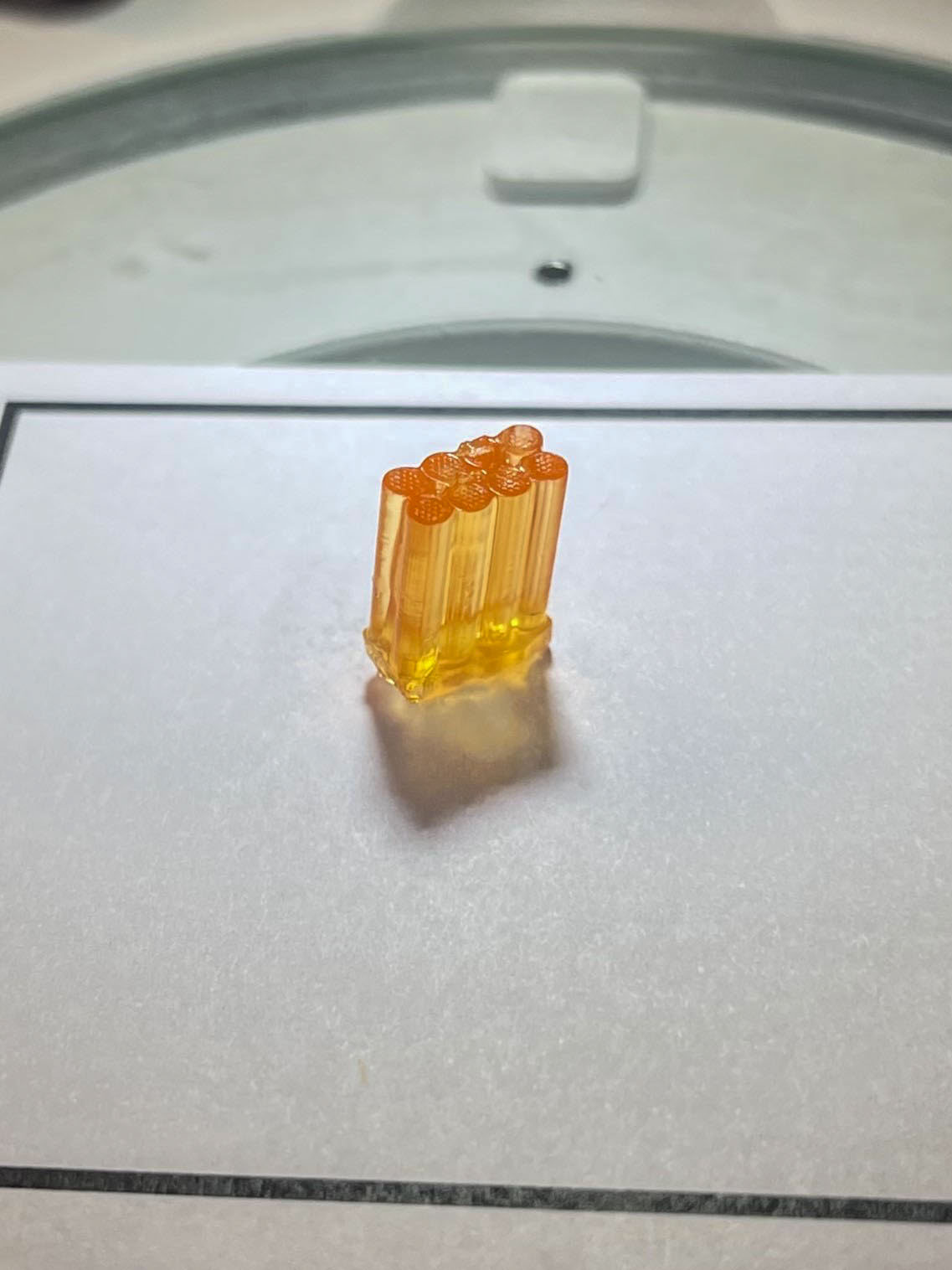
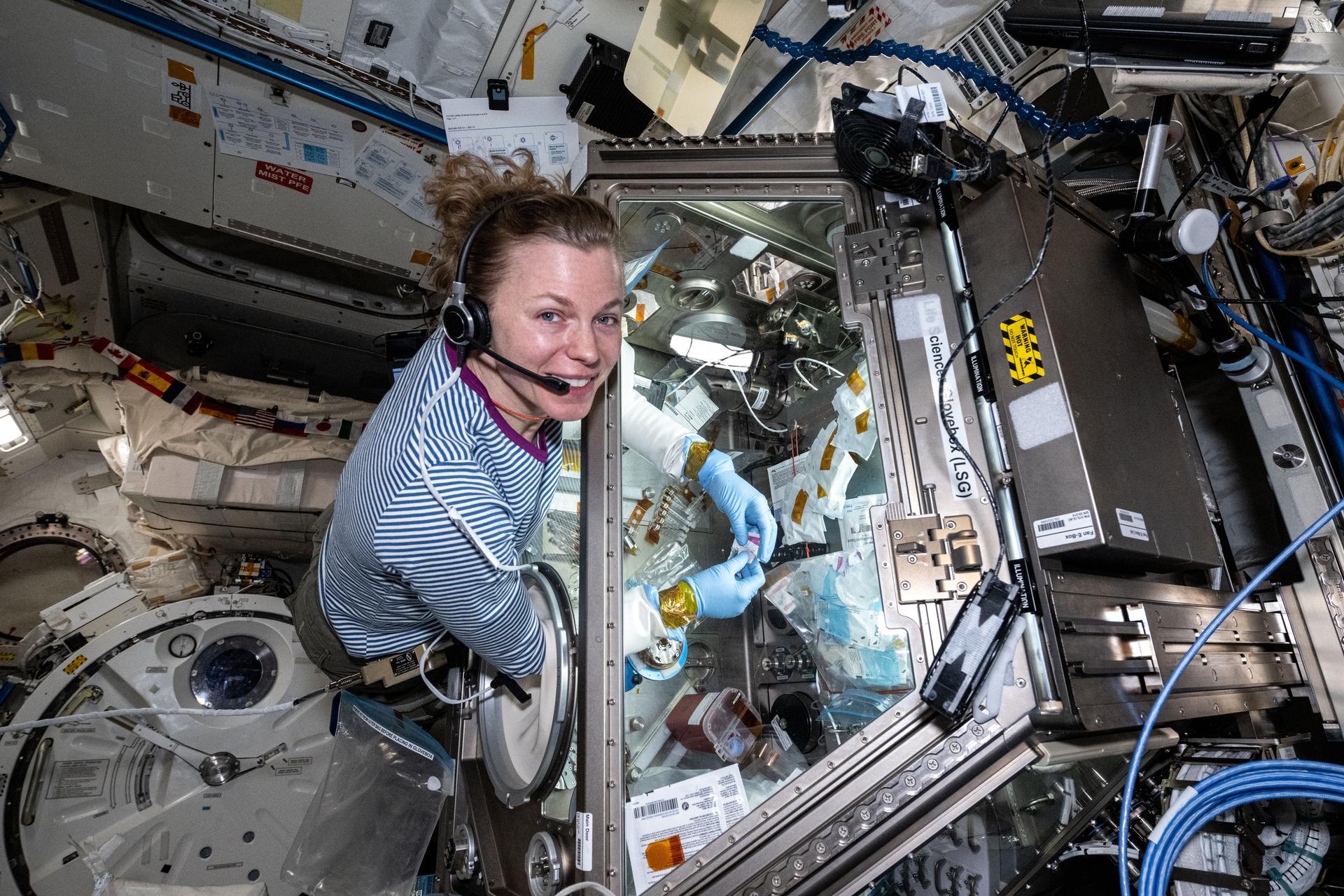
A breakthrough cancer treatment
Research aboard the International Space Station helped inform the development of a newly FDA-approved injectable medication used to treat several types of early-stage cancers. The research yielded early insights into the structure and size of particles needed to develop the medication through protein crystal growth experiments. This new delivery method promises to lower costs and significantly reduce treatment time for patients and healthcare providers, while maintaining drug efficiency. Microgravity research can produce higher-quality, medically relevant crystals than Earth-based labs, enabling these types of medical advances. These developments showcase how space station research can drive innovation, improve lives, and foster commercial opportunities.
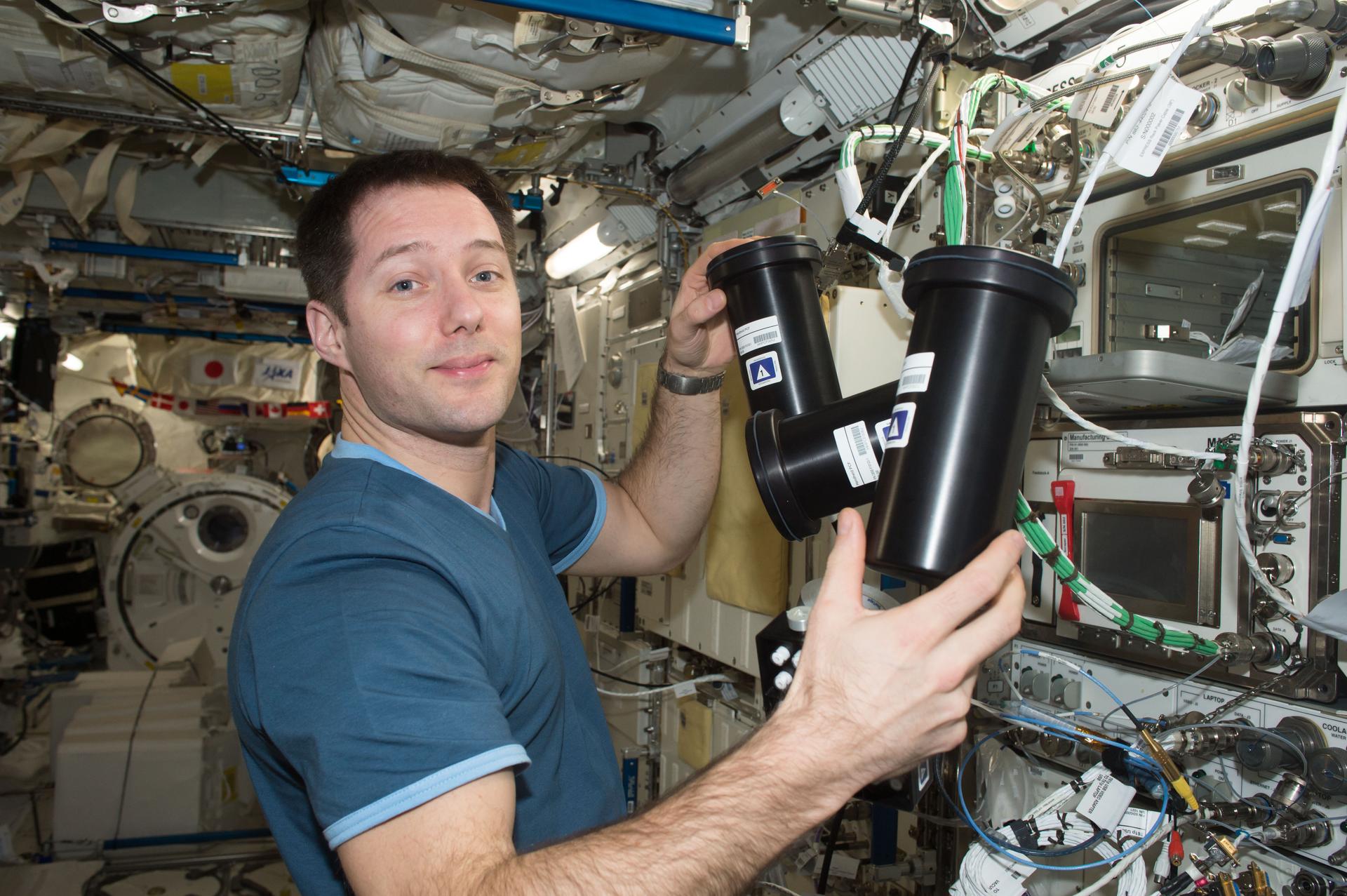
Medical implants printed in orbit
Eight medical implants designed to support nerve regeneration were successfully 3D printed aboard the International Space Station for preclinical trials on Earth. When nerve damage occurs, these types of implants are designed to improve blood flow and enable targeted drug delivery. Printing in microgravity can prevent particle settling, resulting in more uniform and stable structures. In-space manufacturing is helping to advance medical treatments and other technologies while also enabling astronauts to print devices and tools on demand during future missions.
Learn more about InSPA-Auxilium Bioprinter.
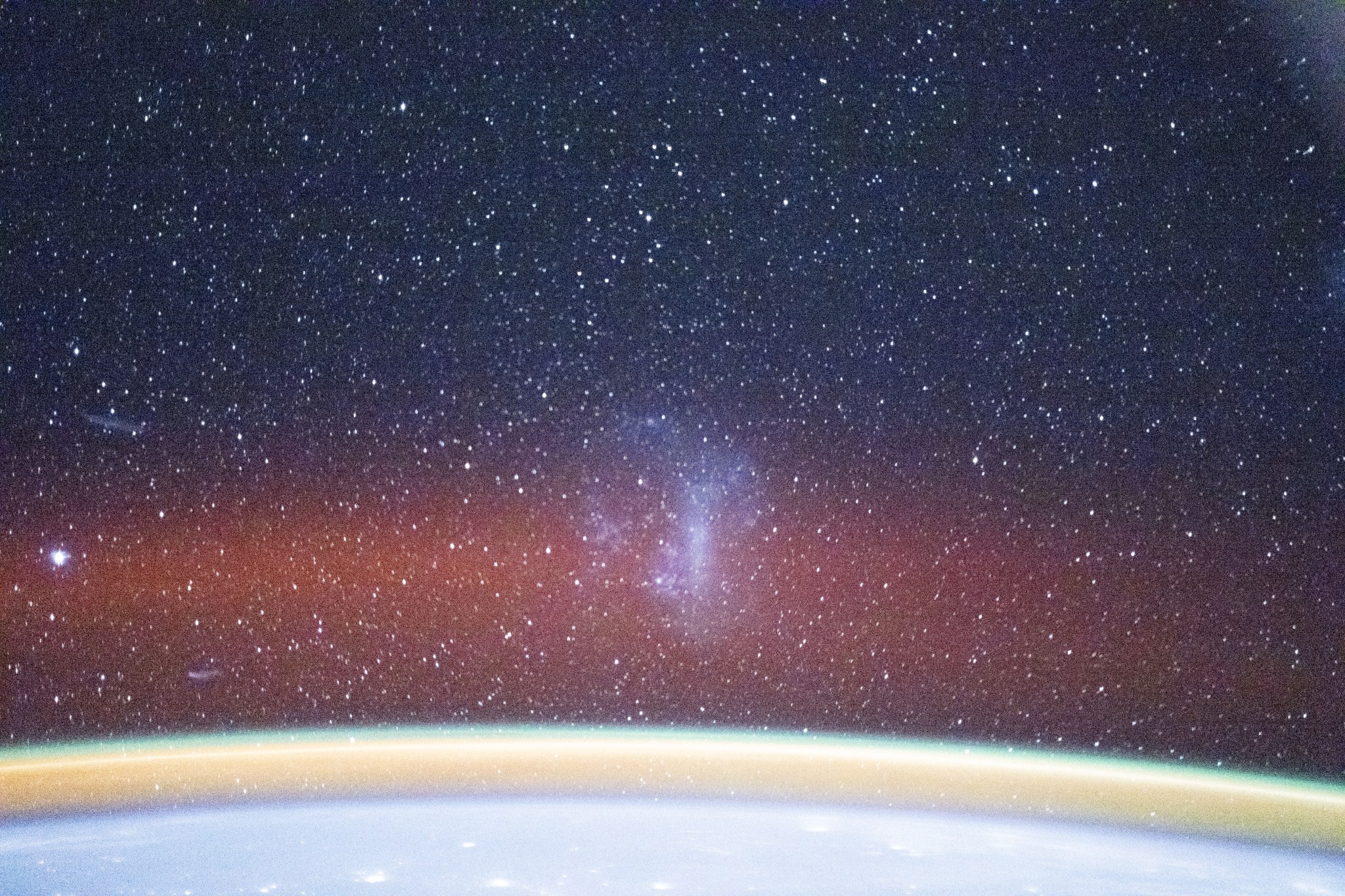
A new understanding of our Sun
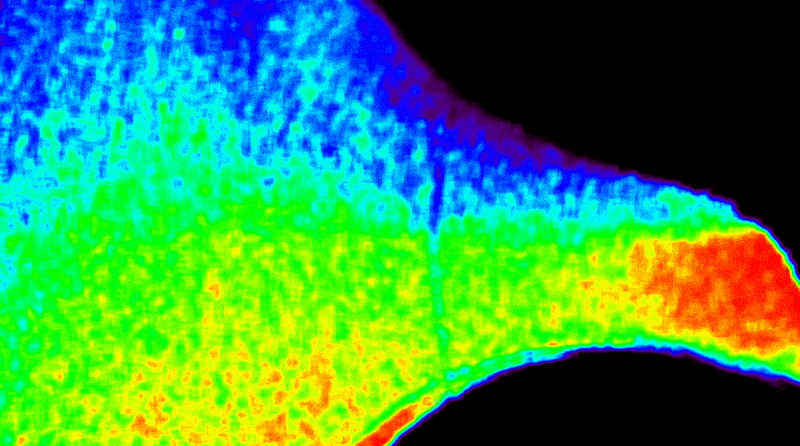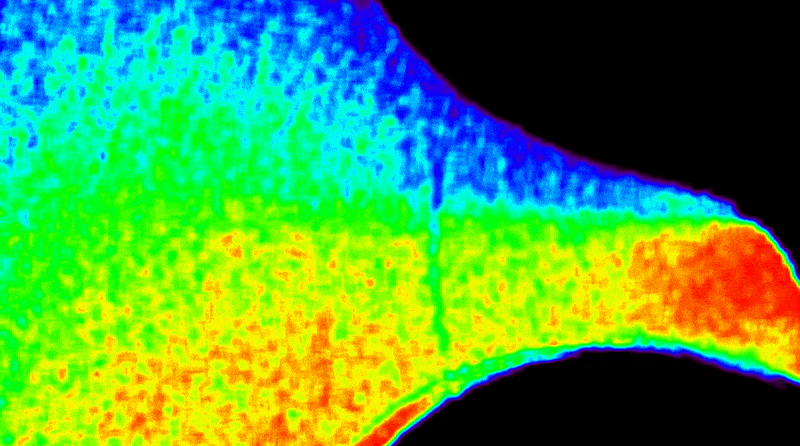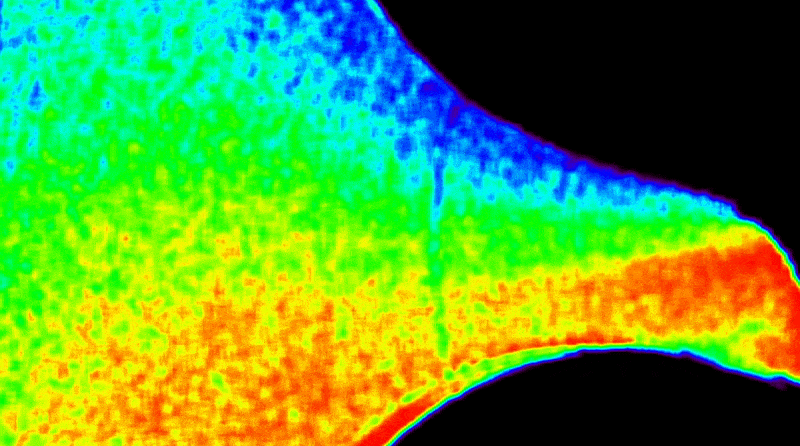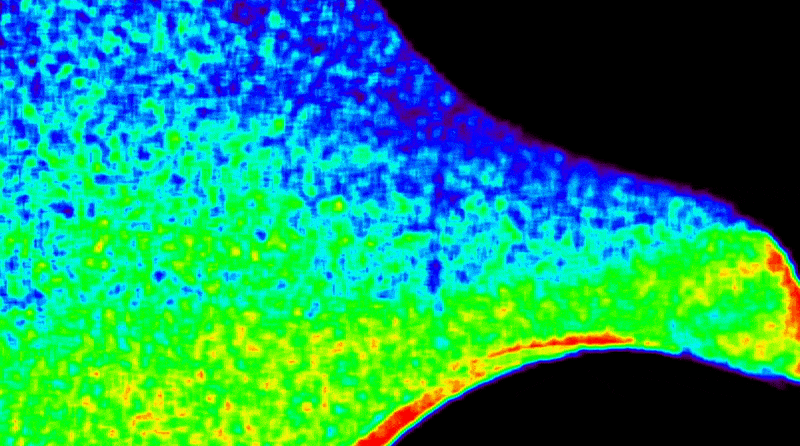

A solar coronagraph aboard the International Space Station captured its first unique images detailing the Sun’s outer atmosphere while measuring solar wind temperature and speed. The instrument blocks the Sun’s bright light to reveal its faint outer atmosphere, or corona, where solar wind originates. Earlier experiments focused on the corona’s density, but this new device enables the study of what heats and accelerates the solar wind, offering a more complete picture of how energy moves through the Sun’s atmosphere. These observations help researchers understand how solar activity affects Earth and space-based technology, such as satellites, communications networks, and power systems.
Learn more about CODEX.
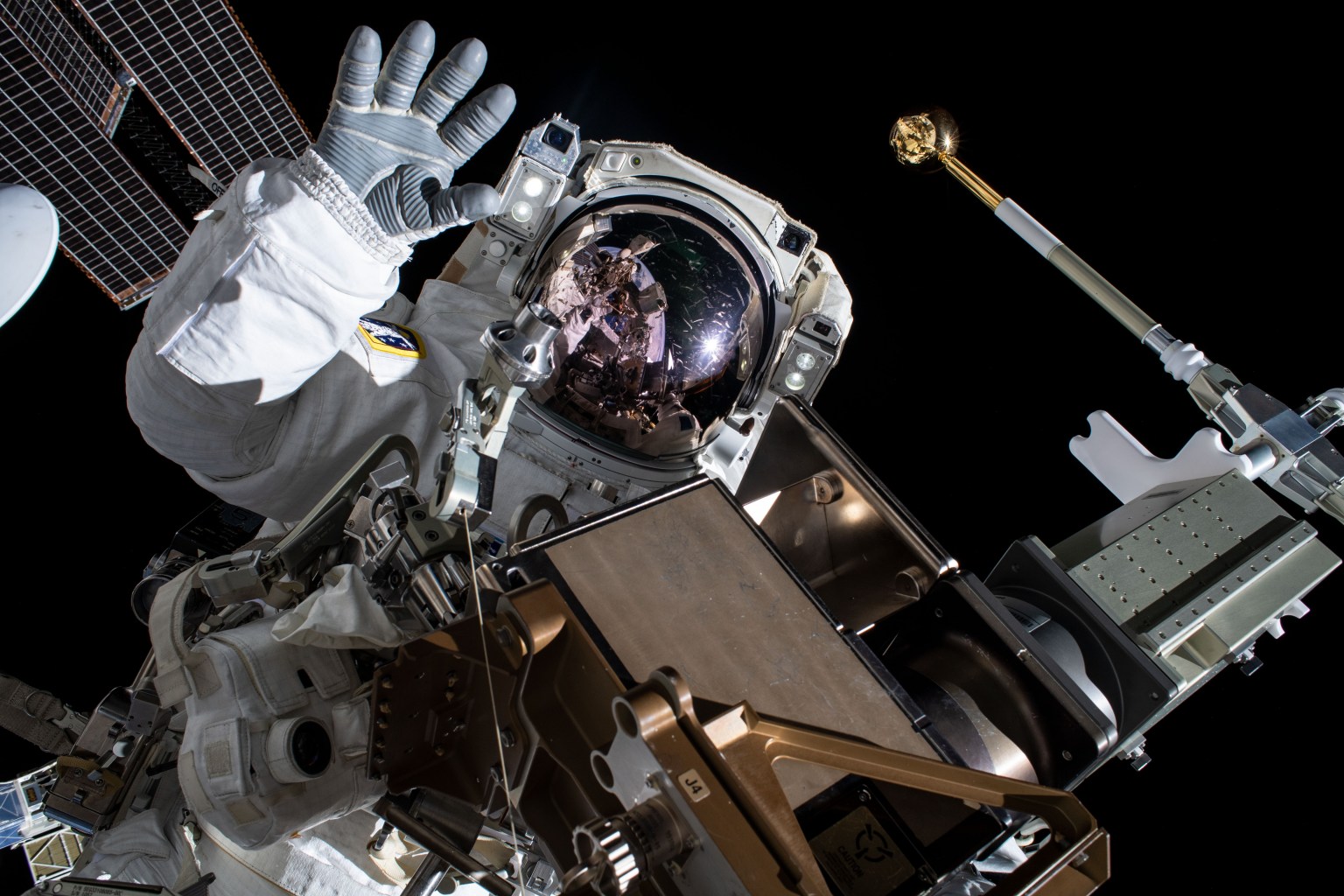
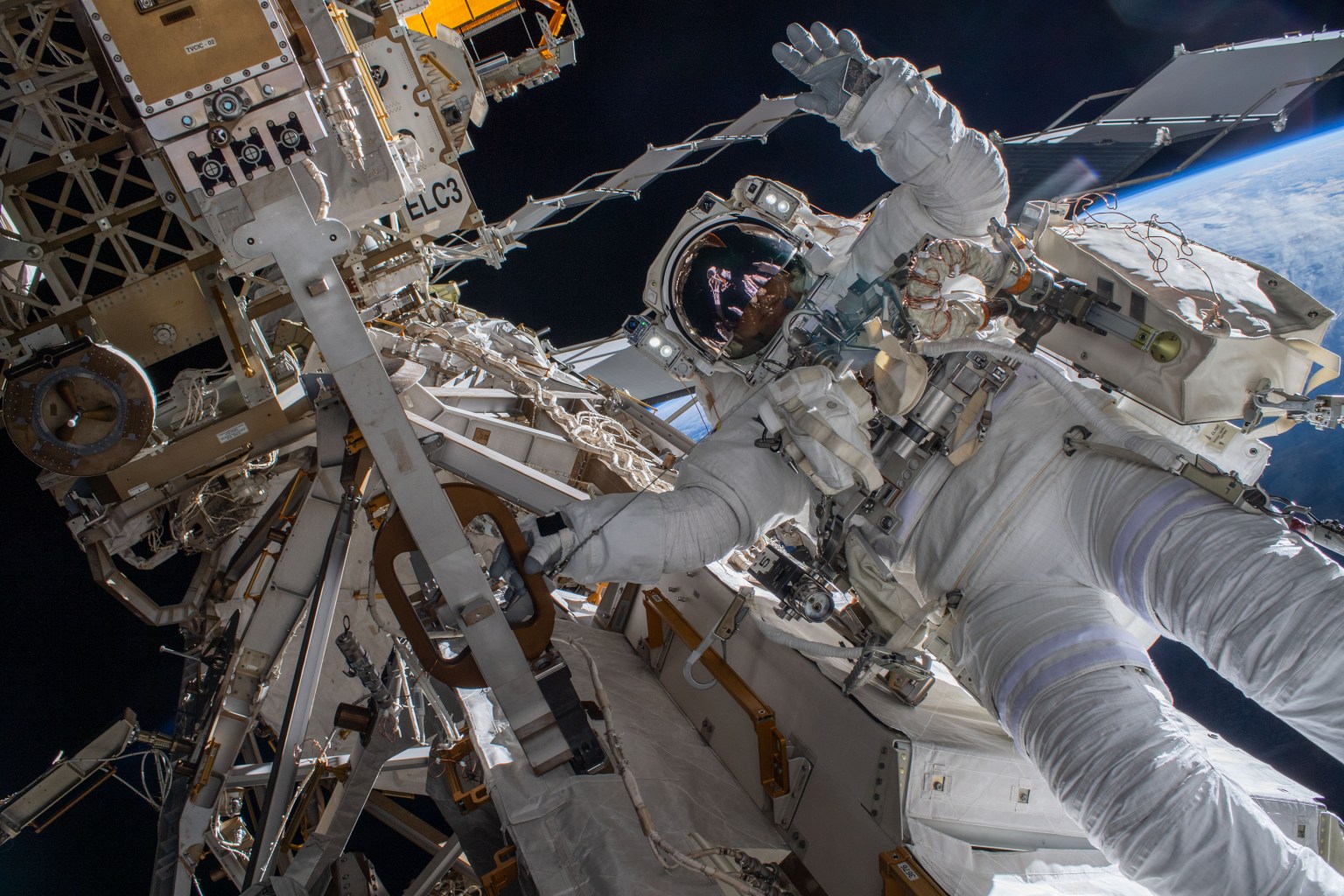
Hunting for microscopic space travelers
NASA astronaut Butch Wilmore collected microbiological samples during a spacewalk outside the International Space Station. Samples were taken near the life support system vents to see if the orbital complex releases microorganisms. This experiment helps researchers examine if and how these microorganisms survive and reproduce in the harsh space environment, as well as how they may behave at destinations such as the Moon and Mars. After returning to Earth, the samples underwent DNA extraction and sequencing. Another round of collections is planned for future spacewalks. The data could help determine whether changes are needed on crewed spacecraft and spacesuits to reduce biocontamination during missions to explore destinations where life may exist now or in the past.
Learn more about ISS External Microorganisms.
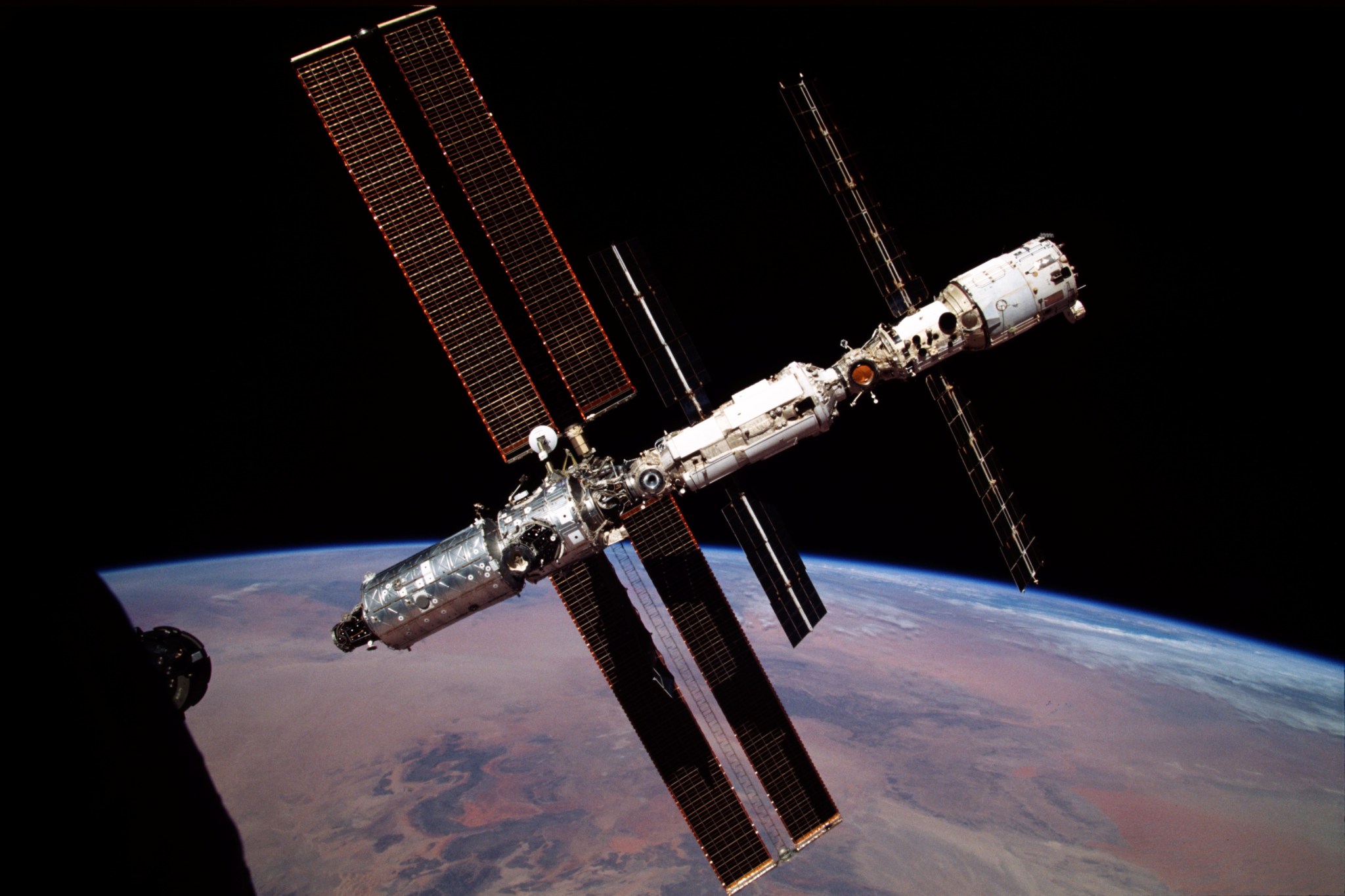
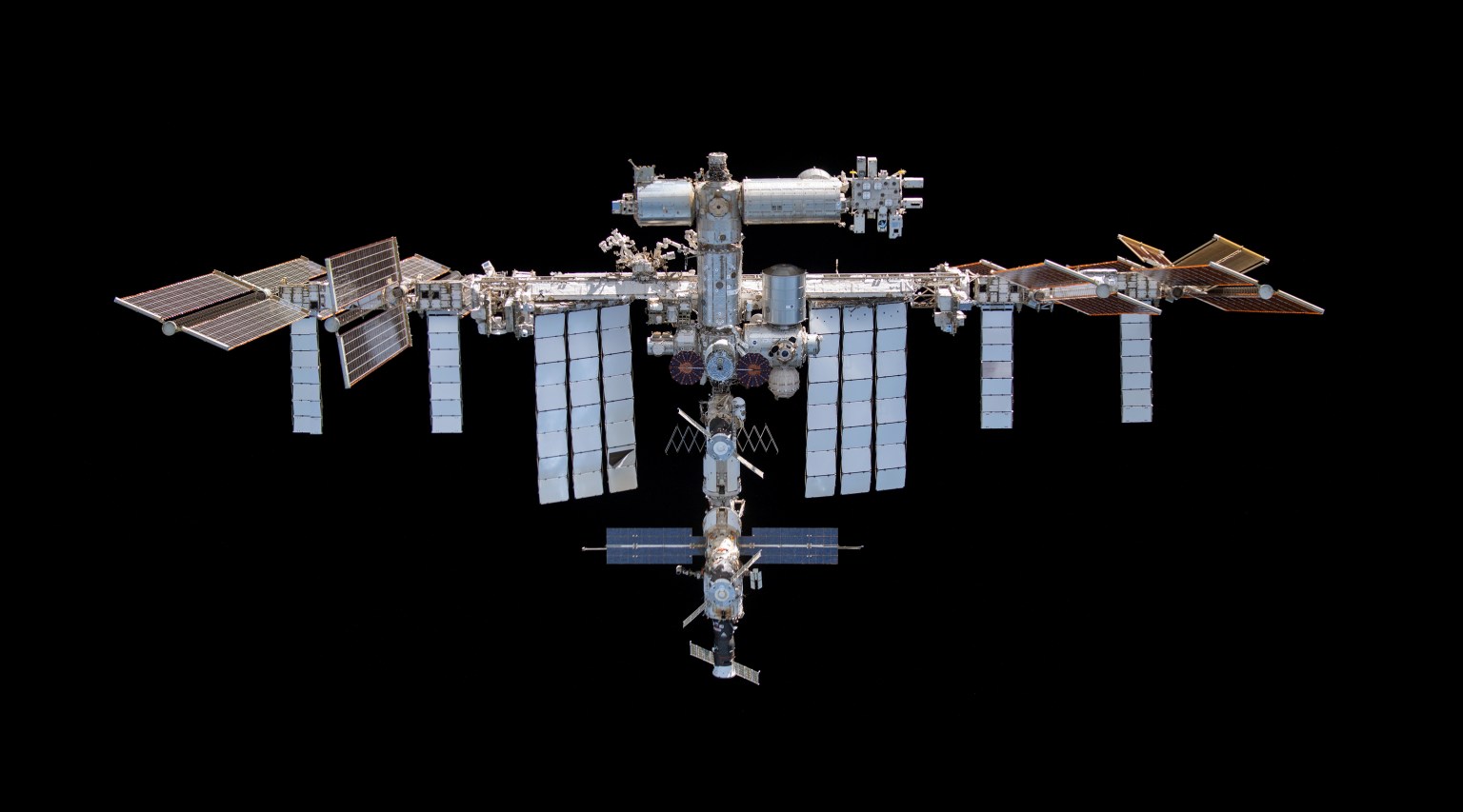
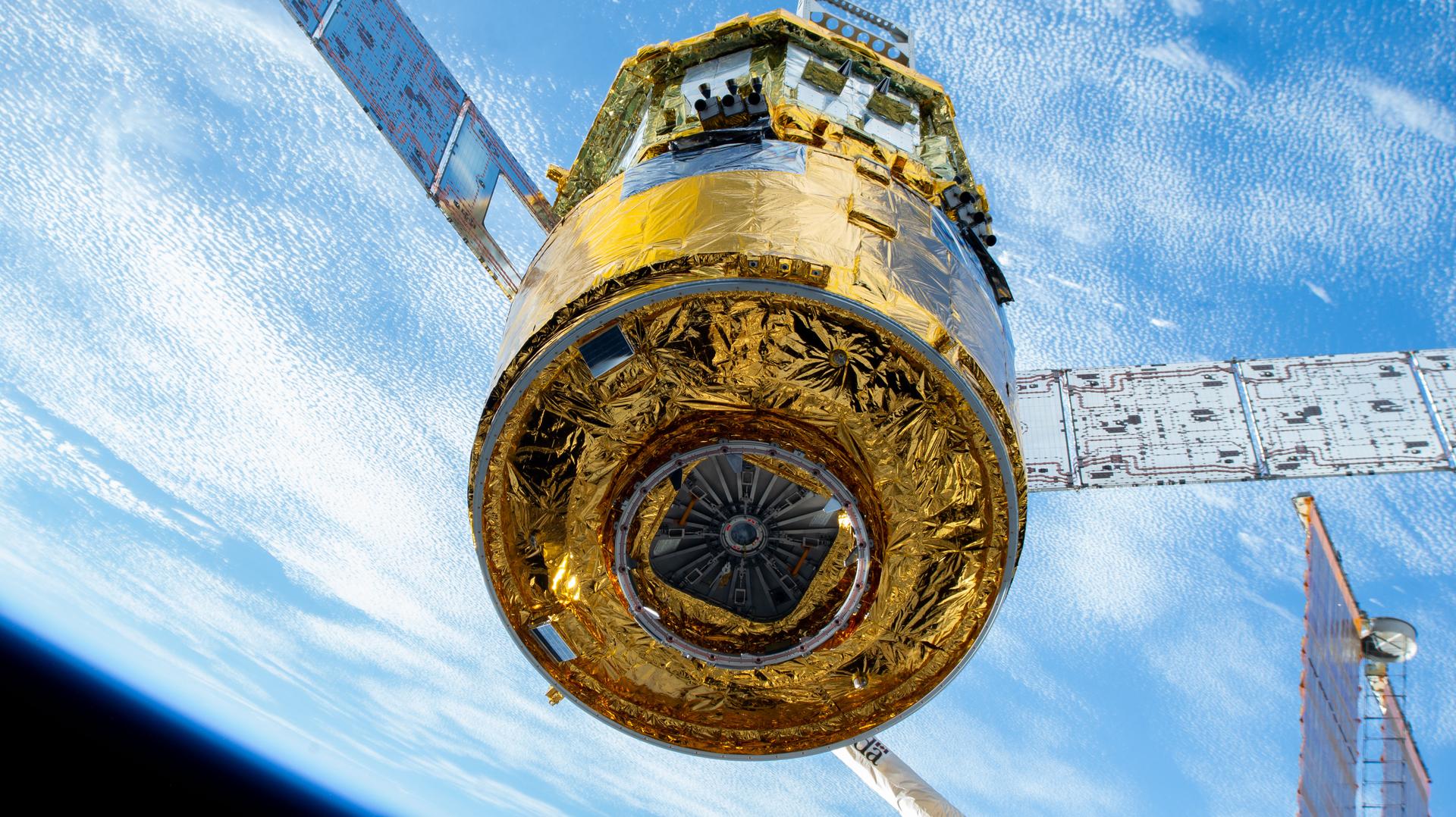
A fully docked space station
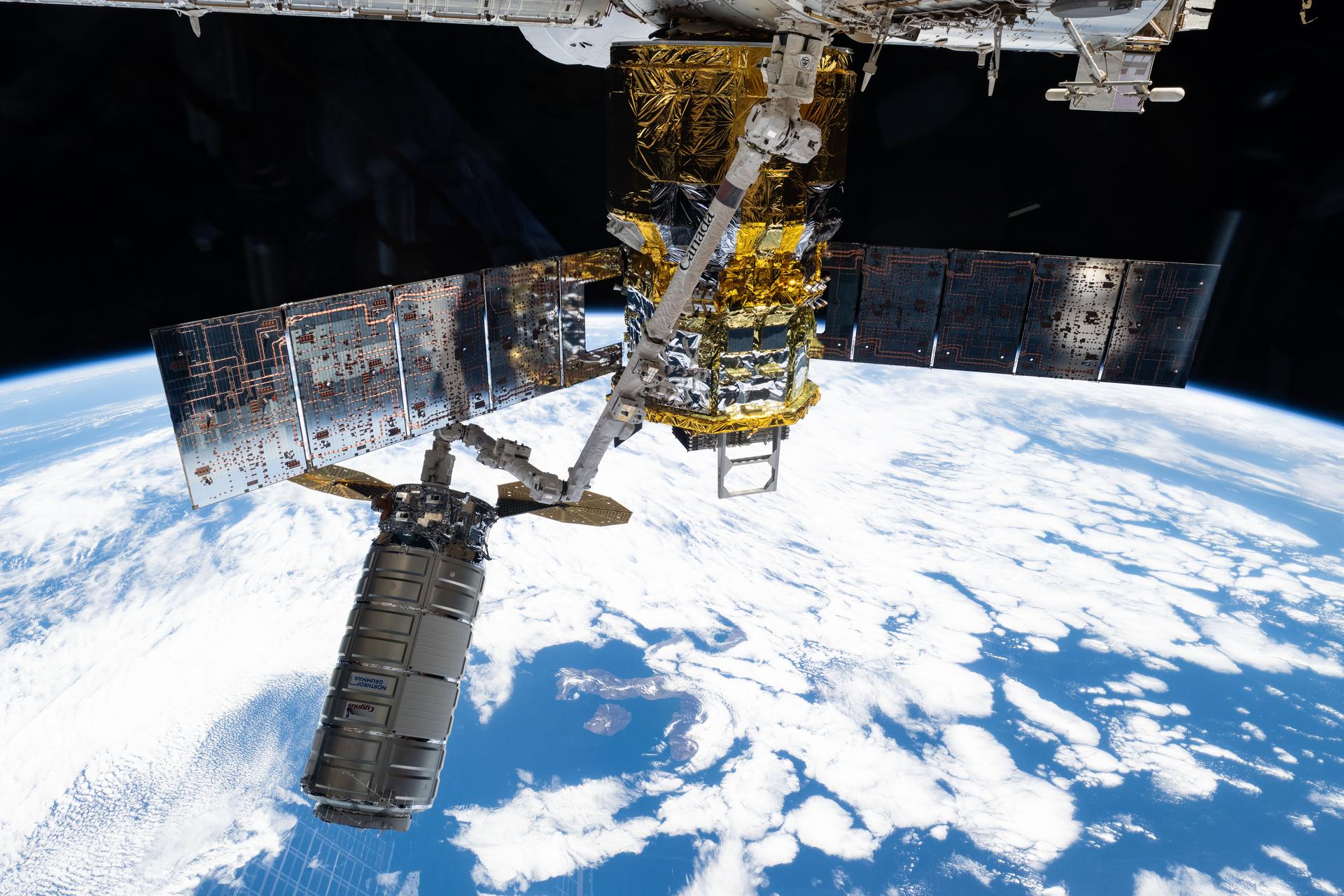

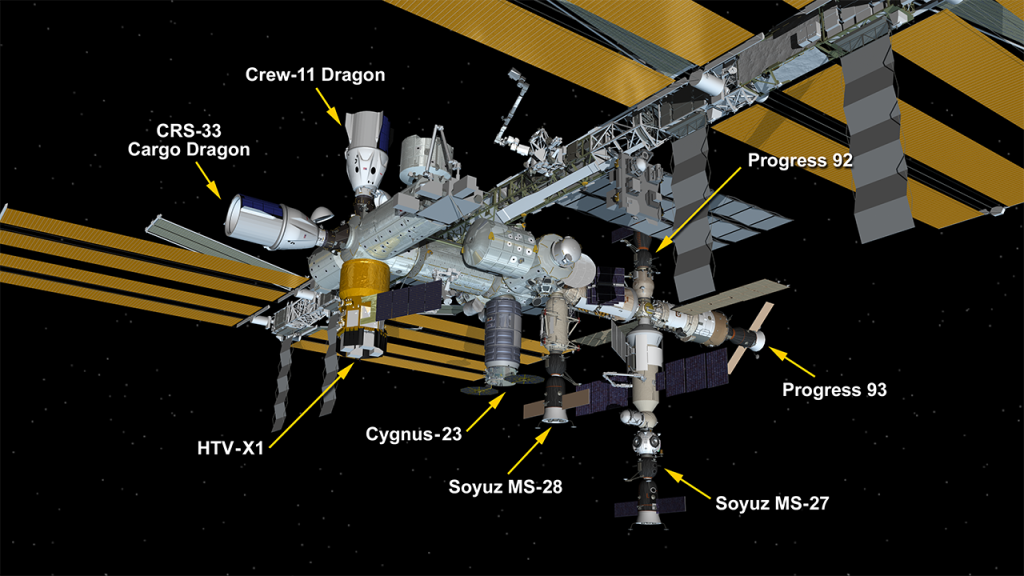
For the first time in International Space Station history, all eight docking ports of the orbiting laboratory were occupied at once. Three crew spacecraft and five cargo resupply craft were attached to station, including JAXA’s new cargo vehicle HTV-X1 and Northrup Grumman’s new Cygnus XL. The eight spacecraft delivered astronauts, cargo, and scientific experiments from around the world to be conducted in the unique microgravity environment. This milestone highlights the space station’s evolution, inviting commercial partners and international collaboration to continue expanding the orbiting laboratory’s research capabilities.
Space station research meets the Moon’s surface
Three experiments that landed on the Moon during Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission-1 were enabled by earlier research aboard the International Space Station. These studies help improve space weather monitoring, test computer recovery from radiation damage, and advance lunar navigation systems. The orbiting laboratory continues to lay the foundation for missions beyond low Earth orbit, driving exploration deeper into space.
Learn more.
The space station continues to deliver out-of-this-world achievements that cannot be replicated on Earth. Its research capabilities are a springboard for humanity’s future in innovation and testing the limits of what’s possible.
Here’s to 2026 — another year of defying physics and pushing the boundaries of science and exploration.